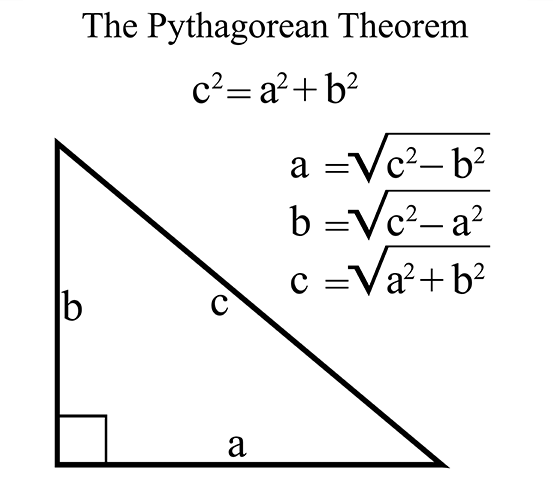

The Pythagorean Theorem is a fundamental principle in geometry that states in a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. Mathematically, it can be expressed as a2 + b2 = c2, where "a" and "b" are the lengths of the legs and "c" is the length of the hypotenuse. This theorem is widely used in various fields to calculate unknown side lengths in right-angled triangles and has significant practical applications in trigonometry, physics, engineering, and more.